MiniBook Logbook Application Manual
1. Introduction
The MiniBook Logbook Application is a user-friendly tool designed to manage your ham radio logbook. It allows you to store, view, and edit your QSO records with ease, while also offering features like file handling, station setup, and logbook management. This manual will guide you through the functions and features available within the program.
2. Key Features
- QSO Management: Add, edit, and delete QSO records.
- Search Functionality: Easily search for specific callsigns or other QSO details.
- File Handling: Load and save logbook files in JSON format (.mbk Minibook files).
- Station Setup: Preset My Callsign, My Locator, and My Location for each QSO.
- QSO Viewing: View, filter, and sort QSO records in a table format.
- Logging: Automatically logs your station setup details with each QSO.
- Import / Export ADIF: Import / Export ADIF format logbooks for use with other logging software or for submission to contests and award programs.
- Rig CAT Support: Makes use of Hamlib, connect your radio direct or remote.
- UDP QSO Log Support: Receive QSO logs from other programs such as WSJT-X
3. User Interface Overview
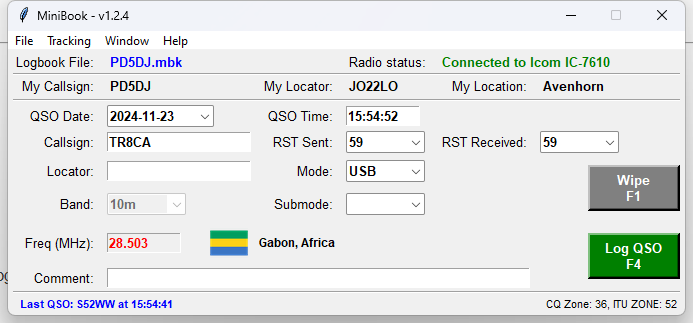
Main Window menu
Upon opening the application, you will see the main window where you can interact with your logbook data.
- Menu Bar:
- File
- Load Logbook: Load a minibook .mbk file
- New Logbook: Create a new minibook file
- Station Setup: When loaded a logbook, Global parameters can be set like, My Callsign, My Locator, My Location. These will be added to each log.
- Preferences:
- Set UTC Offset, add or substract hours from your local time to log the correct UTC time.
- Setup Radio CAT control
- Setup UDP port QSO Logging (WSJT-X)
- Exit: Exit MiniBook
- Tracking
- Date/Time: When Checked, time will be updated every second, You can uncheck if you want to add QSO’s afterwards to set the time manually
- Radio Frequency & Mode: When checked MiniBook will try to connect to your radio or remote Rigctld session
- View
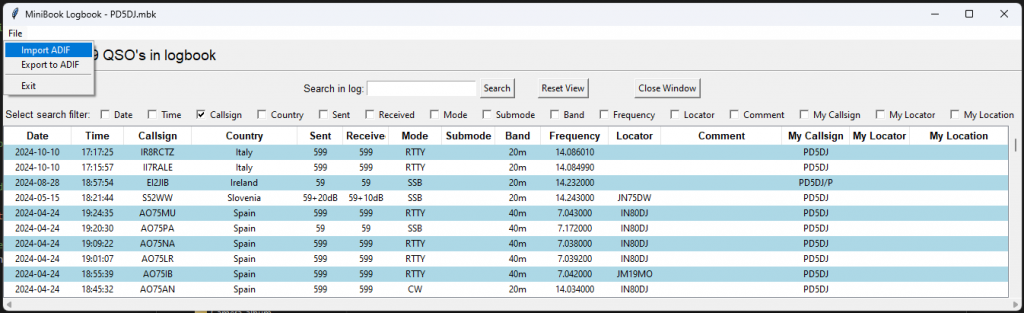
- Logbook: Opens the logbook viewer
- Help
- Key Bindings: Shows keyboard key bindings
- About: Shows About / Info
- File
Main Window
To add a new QSO, click on the “New QSO” button. This will open a form where you can enter details about the QSO, including:
- Date
- Time
- Callsign
- Country
- Sent / Received Reports
- Mode
- Submode
- Band
- Frequency
- Locator
- Comment
QSO Edit Window
To edit an existing QSO, select the record from the logbook viewer and click the “Edit” button. This will allow you to modify any of the fields of the selected QSO record, including:
- Date: The date the QSO took place.
- Time: The time of the QSO.
- Callsign: The callsign of the other station you communicated with.
- Country: The country of the other station.
- Sent: The signal report you sent.
- Received: The signal report you received.
- Mode: The mode used during the QSO (e.g., CW, SSB, etc.).
- Submode: Some Mode’s have sub modes like FT4
- Band: The frequency band used during the QSO.
- Frequency: The specific frequency on which the QSO occurred.
- Locator: The Maidenhead locator of the other station.
- Comment: Any additional comments related to the QSO.
- My Callsign: Your station’s callsign.
- My Locator: Your station’s locator (Maidenhead grid locator).
- My Location: Your physical location or description.
4. Station Setup
The Station Setup section allows you to define key information related to your station that is automatically included in every QSO entry. This ensures consistency across all your QSO records.
My Callsign
This is your station’s callsign, which is used during the QSO and logged with each QSO entry. The callsign entered here will reflect the one used at that time, making it possible to log different callsigns if you operate under different ones at different times.
My Locator
This is your station’s Maidenhead grid locator (e.g., FN31pr). This value is used only for the My Locator field in each QSO, ensuring your grid location is logged with every QSO.
My Location
This is your station’s physical location (e.g., New York, USA). This value is logged in the My Location field for each QSO.
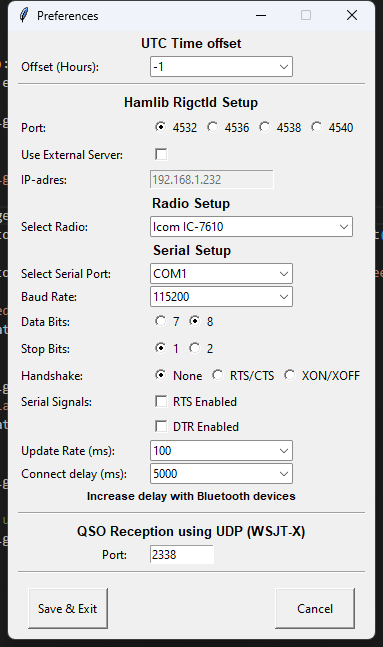
5. Preferences
UTC Offset
Minibook includes a UTC Offset option in the Menu Preferences. This allows you to set your local time zone offset for accurate time logging, ensuring that your QSO entries are recorded with the correct time.
- To access this feature, go to Preferences from the main menu and select the UTC Offset option.
- You can adjust the offset based on your local time zone, ensuring all times are displayed correctly according to your location.
Hamlib Rigctld Setup
It is possible to connect your radio to MiniBook, This allows you to track frequency and mode.
This can be done in 2 ways. Directly through any (bluetooh)serial port. Or remote to another Rigctld server instance.
- Port: default port of Rigctld is 4532, if already occupied you can select any other free port.
- Use External Server: When you want to connect MiniBook to a Rigctld server running on a other machine, enter the IP address of the remote station.
- Radio Setup: When connected directly to MiniBook, you need to select the radio you want to connect with.
- Serial Setup: When connected directly to MiniBook, you need to setup the serial communication between MiniBook and your radio.
- Select Serial Port: Selecting it, will show all available serial ports.
- Baud Rate: Select baudrate that is configured in your radio
- Data Bits / Stop Bits / Handshake: Some older radios need special configuration able to communicate.. by default Data Bits: 8, Stop Bits 1 & Handshake None
- Serial Signals: Some interfaces need RTS or DTR turned on to activate, By default both are OFF
- Update Rate (ms): This is the polling update rate, the frequency Rigctld is requesting frequency and mode from the radio
- Connect delay (ms): Some bluetooth devices need a long time to connect to your computer, try 2000-10000mS
QSO Reception using UDP (WSJT-X)
Minibook is able to listen for incoming QSO log’s sent by other programs such as WSJT-X / JTDX etc..
- Port: select port to listen to, setup same port in WSJT-X / JTDX etc..
6. File Handling
MiniBook offers several features related to managing your logbook files, making it easy to save, load, and work with your QSO data. Below are the key functions available under file handling:
Loading a Logbook
The program can load a logbook in JSON format, also known as .mbk Minibook files. This feature allows you to easily import your QSO records into the program, making it simple to review, edit, and organize your logbook data.
- When you load a .mbk Minibook file, the program reads the contents of the logbook and organizes the data into a structured format.
- The QSO entries are displayed in a tree view, sorted by the date and time of the QSO, so you can quickly find and review your contacts.
- When a logbook file is loaded, the values for My Callsign, My Locator, and My Location from the file are used for the QSO entries, ensuring consistency in the records. These details are saved within the logbook file and can be different across multiple logbook files, allowing you to work with multiple configurations if needed.
Saving and Exporting Logbooks
- After making changes, the program allows you to save the logbook in the .mbk Minibook JSON format, ensuring your QSO records are updated and stored correctly.
Import from ADIF
You can import ADIF files to MiniBook, this makes MiniBook very flexible.
- To Import your logbook to ADIF Format, just click the “Import ADIF” Button and select your ADIF file to import.
- The program will check for new and duplicate QSO’s and convert and import your ADIF file.
- When duplicates are found, you can select to “ignore”, “add”, or “Overwrite” existing QSO’s in your log.
Export to ADIF
You can export your logbook to ADIF format for use with other logging software or for submission to contests and awards. The ADIF (Amateur Data Interchange Format) is a standard format for exchanging QSO data and is widely used by ham radio operators.
- To export your logbook to ADIF, simply select the export option in the menu, choose ADIF as the format, and save the file.
- The program will convert the QSO data from .mbk MiniBook JSON format into the appropriate ADIF tags and structure.
Handling QSO Data
- Each QSO record is stored with key details such as Date, Time, Callsign, Country, Sent, Received, Mode, Band, Frequency, Locator, and Comment.
- The station setup information (My Callsign, My Locator, and My Location) is also included in each entry, ensuring that your station’s details are logged automatically along with the QSO.
- These fields are particularly useful when you operate from different locations, as they can be preset and included in each QSO to reflect your current station setup.
Automatic Updates
- When a logbook is loaded, any changes made to the station configuration (such as My Callsign, My Locator, or My Location) will automatically be reflected in the new QSOs that are logged.
- This ensures that each contact you make is accurately logged with the correct station information, saving you time and effort when operating from different locations.
DXCC Lookup Information
The program utilizes DXCC lookup information, provided by K0SWE. This data is sourced from the repository https://github.com/k0swe/dxcc-json and is used to enrich your QSO records with accurate country and continent information based on the callsign.
7. Managing QSOs
Adding a New QSO
To add a new QSO, you need to open the New QSO Form. Here you can input details like Callsign, Country, Mode, and Frequency. Once all fields are filled out, you can save the entry.
Editing an Existing QSO
To edit an existing QSO, select the entry from the logbook viewer and double click on it. This will open the selected QSO’s details in an editable form, allowing you to update any information.
Deleting a QSO
To delete a QSO, select the record and click the Delete button. The program will ask for confirmation before permanently removing the record.
Search Functionality
You can search for a specific QSO by entering a Callsign or other details in the search bar. The logbook will filter the results to show only matching entries.
Sorting and Filtering
- The logbook entries can be sorted by any field for easier navigation.
- Filtering options allow you to view specific entries based on Callsign, Country, Mode, or other criteria.
8. Troubleshooting
Program Errors
If you encounter errors when loading or saving files, ensure that your JSON or .mbk Minibook file is properly formatted. You may also check the application’s error messages for specific issues.
Missing QSO Entries
If some QSO entries are missing after loading a file, ensure that the file is in the correct format and that all required fields (such as Date, Time, and Callsign) are present in the logbook.
Date/Time Errors
If the program fails to process date and time correctly, double-check the date format in the loaded file. The program expects dates in the format YYYY-MM-DD and time in HH:MM
Bugs or Errors
If any errors or bugs are found, please contact me for assistance. I will be happy to help resolve any issues you encounter..
9. Conclusion
The MiniBook Logbook Application is designed to streamline the process of logging, editing, and managing your ham radio QSO records. With robust features like station setup management, QSO editing, file handling, and ADIF export, the application provides a comprehensive tool for amateur radio operators to keep their logbooks organized and accurate.